SECTION II
Number of questions: 55
DIRECTIONS for questions 56 to 74: Answer each of the questions independently.
56. The number of positive integer valued pairs (x, y), satisfying 4x - 17 y = I and x < 1000 is:
1. 59
2. 57
3. 55
4. 58
57. Let a, b, c be distinct digits. Consider a two digit number 'ab' and a three digit number 'ccb', both defined under the usual decimal number system. If
(ab)2 = ccb and ccb > 300 then the value of b is
1. 1
2. 0
3. 5
4. 6
58. The remainder when 784 is divided by 342 is :
1. 0
2. 1
3. 49
4. 341
59. Ten points are marked on a straight line and eleven points are marked on another straight line. How many triangles can be constructed with vertices from among the above points?
1. 495
2. 550
3. 1045
4. 2475
60. For a scholarship, at most n candidates out of 2n + I can be selected. If the number of different ways of selection of at least one candidate is 63, the maximum number of candidates that can be selected for the scholarship is:
1. 3
2. 4
3. 2
4. 5
61. The speed of a railway engine is 42 Km per hour when no compartment is attached, and the reduction in speed is directly proportional to the square root of the number of compartments attached. If the speed of the train carried by this engine is 24 Km per hour when 9 compartments are attached, the maximum number of
compartments that can be carried by the engine is:
1. 49
2. 48
3. 46
4. 47
62. Total expenses of a boarding house are partly fixed and partly varying linearly with tile number of boarders. The average expense per boarder is Rs. 700 when there are 25 boarders and Rs. 600 when there are 50 boarders. What is the average expense per boarder when there are 100 boarders?
1. 550
2. 560
3. 540
4. 560
63. Forty percent of the employees of a certain company are men, and 75 percent of the men more than Rs. 25,000 per year. If 45 percent of the company's employees earn more than Rs. 25,000 per year, what fraction of the women employed by the company earn Rs. 25,000 year or less'?
1. 2/11
2. ¼
3. 1/3
4. ¾
64. If | r - 6 | = 11 and | 2q - 12 | = 8, what is the minimum possible value of q / r?
1. -2/5
2. 2/17
3. 10/17
4. None of these
65. If n = 1 + x, where x is the product of four consecutive positive integers, then which of the following is/are true?
A. n is odd
B. n is prime
C. n is a perfect square
1. A and C only
2. A and B only
3. A only
4. None of these
66. In a survey of political preference, 78% of those asked were in favor of at least one of the proposals: I, II and III. 50% of those asked favored proposal I, 30% favored proposal II, and 20% favored proposal III. If 5% of those asked favored all three of the proposals, what percentage of those asked favored more than one of the 3 proposals.
1. 10
2. 12
3. 17
4. 22
67. For two positive integers a and b define the function h(a,b) as the greatest common factor (gdf) of a, b. Let A be a set of n positive integers. G( A), the gcf of the elements of set A is computed by repeatedly using the function h. The minimum number of times h is required to be used to compute G is:
1. ½ n
2. (n - 1)
3. n
4. None of these
 68. The figure below shows two concentric circles with centre 0. PQRS is a square, inscribed in the outer circle. It also circumscribes the inner circle, touching it at points B, C, D and A. What is the ratio of the perimeter of the outer circle to that of polygon ABCD?
68. The figure below shows two concentric circles with centre 0. PQRS is a square, inscribed in the outer circle. It also circumscribes the inner circle, touching it at points B, C, D and A. What is the ratio of the perimeter of the outer circle to that of polygon ABCD?
1.  / 4 / 4
2. 3 / 2 / 2
3.  / 2 / 2
4. 
69. Three labeled boxes containing red and white cricket balls are all mislabeled. It is known that one of the boxes contains only white balls and one only red balls. The third contains a mixture of red and white balls. You are required to correctly label the boxes with the labels red, white and red and white by picking a sample of one ball from only one box. What is the label on the box you should sample?
1. White
2. Red
3. Red and White
4. Not possible to determine from a sample of one ball
70. If n2 = 123456787654321, what is n?
1. 12344321
2. 1235789
3. 11111111
4. 1111111
71. Abraham, Border, Charlie, Dennis and Elmer and their respective wives recently dined together and were seated at a circular table. The seats were so arranged that men and women alternated and each woman was three places distant from her husband. Mrs. Charlie sat to the left of Mr. Abraham. Mrs. Elmer sat two places to the right of Mrs. Border. Who sat to the right of Mr. Abraham?
1. Mrs. Dennis
2. Mrs. Elmer
3. Mrs. Border
4. Mrs. Border or Mrs. Dennis
72. Navjivan Express from Ahmedabad to Chennai leaves Ahmedabad at 6:30 am and travels at 50km per hour towards Baroda situated 100 kms away. At 7:00 am Howrah - Ahmedabad express leaves Baroda towards Ahmedabad and travels at 40 km per hour. At 7:30 Mr. Shah, the traffic controller at Baroda realises that both the trains are running on the same track. How much time does he have to avert a head-on collision between the two trains?
1. 15 minutes
2. 20 minutes
3. 25 minutes
4. 30 minutes
73. There is a circle of radius 1 cm. Each member of a sequence of regular polygons S1(n), n = 4,5,6,... , where n is the number of sides of the polygon, is circumscribing the circle; and each member of the sequence of regular polygons S2(n), n = 4,5,6.... where n is the number of sides of the polygon, is inscribed in the circle. Let L1(n) and L2(n) denote the perimeters of the corresponding polygons of S1(n) and S2(n).
Then {L1(13) + 2 } / L2(17) is } / L2(17) is
1. greater than  / 4 and less than 1 / 4 and less than 1
2. greater than 1 and less than 2
3. greater than 2
4. less than  / 4 / 4
74. There is a square field with each side 500 metres long. It has a compound wall along its perimeter. At one of its comers, a triangular area of the field is to be cordoned off by erecting a straight line fence. The compound wall and the fence will form its borders. If the length of the fence is 100 metres, what is the maximum area in square metres that can be cordoned off?
1. 2,500
2. 10,000
3. 5,000
4. 20,000
DIRECTIONS for questions 75 to 77: These questions are based on the situation given below:
Ten coins are distributed among four people P, Q, R, S such that one of them gets one coin, another gets two coins, the third gets three coins and the fourth gets four coins. It is known that Q gets more coins than P, and S gets fewer coins than R.
75. If the number of coins distributed to Q is twice the number distributed to P then which one of the following is necessarily true?
1. R gets an even number of coins.
2. R gets an odd number of coins.
3. S gets an even number of coins.
4. S gets an odd number of coins.
76. If R gets at least two more coins than S, then which one of the following is necessarily true?
1. Q gets at least two more coins than S.
2. Q gets more coins than P.
3. P gets more coins than S.
4. P and Q together get at least five coins.
77. If Q gets fewer coins than R, then which one of the following is not necessarily true?
1. P and Q together get at least four coins.
2. Q and S together get at least four coins.
3. R and S together get at least five coins.
4. P and R together get at least five coins.
DIRECTIONS for questions 78 to 80: These questions are based on the situation given below:
A young girl Roopa leaves home with x flowers, goes to the bank of a nearby river. On the bank of the river, there are four places of worship, standing in a row. She dips all the x flowers into the river. The number of flowers doubles. Then she enters the first place of worship, offers y flowers to the deity. She dips the remaining flowers into the river, and again the number of flowers doubles. She goes to the second place of worship, offers y flowers to the deity. She dips the remaining flowers into the river, and again the number of flowers doubles. She goes to the third place of worship, offers y flowers to the deity. She dips the remaining flowers into the river, and again the number of flowers doubles. She goes to the fourth place of worship, offers y flowers to the deity. Now she is left with no flowers in hand.
78. If Roopa leaves home with 30 flowers, the number of flowers she offers to each deity is:
1. 30
2. 31
3. 32
4. 33
79. The minimum number of flowers that could be offered to each deity is:
1. 0
2. 15
3. 16
4. Cannot be determined
80. The minimum number of flowers with which Roopa leaves home is:
1. 16
2. 15
3. 0
4. Cannot be determined
DIRECTIONS for questions 81 and 82: The following table presents the sweetness of different items relative to sucrose, whose sweetness is taken to be 1.00.
| Lactose |
0.163 |
| Maltose |
0.32 |
| Glucose |
0.74 |
| Sucrose |
1.00 |
| Fructose |
1.70 |
| Saccharin |
675.00 |
81. What is the minimum amount of sucrose (to the nearest gram) that must be added to one-gram of saccharin to make a mixture that will be at least I 00 times as sweet as glucose?
1. 7
2. 8
3. 9
4. 100
82. Approximately how many times sweeter than sucrose is a mixture consisting of glucose, sucrose and fructose in the ratio of 1: 2: 3?
1. 1.3
2. 1
3. 0.6
4. 2.3
DIRECTIONS for questions 83 and 84: These questions are based on the situation given below:
A, B, C, D, E and F are a group of friends from a club. There are two housewives, one lecturer, one architect, one accountant and one lawyer in the group. There are two married couples in the group. The lawyer is married to D who is a housewife. No lady in the group is either an architect or an accountant. C, the accountant, is married to F who is a lecturer. A is married to D and E is not a housewife.
83. What is E?
1. Lawyer
2. Architect
3. Lecturer
4. Accountant
84. How many members of the group are male?
1. 2
2. 3
3. 4
4. None of these
DIRECTIONS for questions 85 and 86: These questions are based on the situation given below:
Seven university cricket players are to be honored at a special luncheon. The players will be seated on the dais along one side of a single rectangular table.
A and G have to leave the luncheon early and must be seated at the extreme right end of the table, which is closest to the exit.
B will receive the Man of the Match award and must be in the center chair.
C and D who are bitter rivals for the position of wicket keeper, dislike one another and should be seated as far apart as possible.
E and F are best friends and want to sit together.
85. Which of the following may not be seated at either end of the table?
1. C
2. D
3. G
4. F
86. Which of the following pairs may not be seated together?
1. E & A
2. B & D
3. C & F
4. G & D
DIRECTIONS for questions 87 and 88: These questions are based on the situation given below:
A rectangle PRSU, is divided into two smaller rectangles PQTU, and QRST by the line TQ. PQ=10cm, QR = 5 cm and RS = 10 cm. Points A, B, F are within rectangle PQTU, and points C, D, E are within the rectangle QRST. The closest pair of points among the pairs (A, C), (A, D), (A, E), (F, C), (F, D), (F, E), (B, C), (B, D), (B, E) are 10 cm apart. cm apart.
87. Which of the following statements is necessarily true?
1. The closest pair of points among the six given points cannot be (F, C)
2. Distance between A and B is greater than that between F and C
3. The closest pair of points among the six given points is (C, D), (D, E), or (C, E)
4. None of the above
88. AB > AF > BF; CD > DE > CE; and BF = 6 cm. Which is the closest pair of points among all the six given points? cm. Which is the closest pair of points among all the six given points?
1. B, F
2. C, D
3. A, B
4. None of these
DIRECTIONS for questions 89 to 92: These questions are based on the situation given below:
In each of the questions 89 to 92 a pair of graphs F(x) and F1(x) is given. These are composed of straight-line segments, shown as solid lines, in the domain x  (-2, 2). (-2, 2).
If F1(x) = - F(x) choose the answer as a;
if F1(x) = F(- x) choose the answer as b;
if F1(x) = - F(- x) choose the answer as c;
and if none of the above is true, choose the answer as d;
89.

1. a
2. b
3. c
4. d
90.

1. a
2. b
3. c
4. d
91.

1. a
2. b
3. c
4. d
92.

1. a
2. b
3. c
4. d
DIRECTIONS for questions 93 and 94: These questions are based on the situation given below:
There are in blue vessels with known volumes V1, V2 , ...., Vm, arranged in ascending order of volume, where v1 > 0.5 litre, and vm < 1 litre. Each of these is full of water initially. The water from each of these is emptied into a minimum number of empty white vessels, each having volume 1 litre. The water from a blue vessel is not emptied into a white vessel unless the white vessel has enough empty volume to hold all the water of the blue vessel. The number of white vessels required to empty all the blue vessels according to the above rules was n.
93. Among the four values given below, which is the least upper bound on e, where e is the total empty volume in the n white vessels at the end of the above process?
1. mvm
2. m(1 - vm)
3. mv1
4. m(1 - v1)
94. Let the number of white vessels needed be n1 for the emptying process described above, if the volume of each white vessel is 2 liters. Among the following values, which is the least upper bound on n1?
1. m/4
2. smallest integer greater than or equal to (n/2)
3. n
4. greatest integer less than or equal to (n/2)
DIRECTIONS for questions 95 to 97: These questions are based on the situation given below:
There are fifty integers a1, a2,...,a50, not all of them necessarily different. Let the greatest integer of these fifty integers be referred to as G, and the smallest integer be referred to as L. The integers a1 through a24 form sequence S1, and the rest form sequence S2. Each member of S1 is less than or equal to each member of S2.
95. All values in S1 are changed in sign, while those in S2 remain unchanged. Which of the following statements is true?
1. Every member of S1 is greater than or equal to every member of S2.
2. G is in S1
3. If all numbers originally in S1 and S2 had the same sign, then after the change of sign, the largest number of S1 and S2 is in S1.
4. None of the above
96. Elements of S1 are in ascending order, and those of S2 are in descending order. a24 and a25 are interchanged. Then, which of the following statements is true?
1. S1 continues to be in ascending order
2. S2 continues to be in descending order
3. S1 continues to be in ascending order and S2 in descending order.
4. None of the above
97. Every element of S1 is made greater than or equal to every element of S2 by adding to each element of S1 an integer x. Then x cannot be less than:
1. 210
2. The smallest value of S2
3. The largest value of S2
4. ( G-L )
DIRECTIONS for questions 98 to 100: These questions are based on the situation given below:
Let x and y be real numbers and let
f(x, y) = | x + y |, F(f(x, y)) = -f(x, y) and G(f(x, y)) = -F(f(x, y))
98. Which of the following statements is true?
1. F(f(x, y)) . G(f(x, y)) = -F(f(x, y)) . G(f(x, y))
2. F(f(x, y)) . G(f(x, y)) > -F(f(x, y)) . G(f(x, y))
3. F(f(x, y)) . G(f(x, y)) 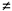 G(f(x, y)) . F(f(.x, y)) G(f(x, y)) . F(f(.x, y))
4. F(f(x,y)) + G(f(x, y)) + f(x, y) = f(-x, -y)
99. What is the value of f(G(f(1, 0)), f(F(f(1, 2)), G(f(1, 2))))?
1. 3
2. 2
3. 1
4. 0
100. Which of the following expressions yields x2 as its result?
1. F(f(x, -x)).G(f(x, -x))
2. F(f(x, x)).G(f(x, x)).4
3. -F(f(x, x).G(f(x, x))  log2 16 log2 16
4. f(x, x).f(x, x)
DIRECTIONS for questions 101 and 102: These questions are based on the situation given below:
A robot moves on a graph sheet with x and y-axes. The robot is moved by feeding it with a sequence of instructions. The different instructions that can be used in moving it, and their meanings are:
| Instruction |
Meaning |
| GOTO(x,y) |
move to point with coordinates (x, y) no matter where you are currently |
| WALKX(P) |
Move parallel to the x-axis through a distance of p, in the positive
direction if p is positive, and in the negative direction if p is negative |
| WALKY(P) |
Move parallel to the y-axis through a distance of p, in the positive
direction if p is positive, and in the negative direction if p is negative. |
101. The robot reaches point (6, 6) when a sequence of three instructions is executed, the first of which is a GOTO(x, y) instruction, the second is WALKX(2) and the third is WALKY(4). What are the values of x and y?
1. 2, 4
2. 0, 0
3. 4, 2
4. 2, 2
102. The robot is initially at (x, y), x > 0 and y < 0. The minimum number of instructions needed to be executed to bring it to the origin (0,0) if you are prohibited from using the GOTO instruction is:
1. 2
2. 1
3. x + y
4. 0
DIRECTIONS for questions 103 to 105: These questions are based on the situation given below:
A road network (shown in the figure below) connects cities A, B, C and D. All road segments are straight lines. D is the midpoint on the road connecting A and C. Roads AB and BC are at right angles to each other with BC shorter than AB. The segment AB is 100 km long.
 Ms. X and Mr. Y leave A at 8:00 am, take different routes to city C and reach at the same time. X takes the highway from A to B to C and travels at an average speed of 61.875 km per hour. Y takes the direct route AC and travels at 45 km per hour on segment AD. Y's speed on segment DC is 55 km per hour.
Ms. X and Mr. Y leave A at 8:00 am, take different routes to city C and reach at the same time. X takes the highway from A to B to C and travels at an average speed of 61.875 km per hour. Y takes the direct route AC and travels at 45 km per hour on segment AD. Y's speed on segment DC is 55 km per hour.
103. What is the average speed of Y in km per hour?
1. 47.5
2. 49.5
3. 50
4. 52
104. The total distance traveled by Y during the journey is approximately
1. 105 km
2. 150 km
3. 130 km
4. Cannot be determined
105. What is the length of the road segment BD?
1. 50 km
2. 52.5 km
3. 55 km
4. Cannot be determined
DIRECTIONS for questions 106 and 107: These questions are based on the situation given below:
 Rajiv reaches city B from city A in 4 hours, driving at the speed of 35 km per hour for the first 2 hours and at 45 km per hour for the next two hours. Aditi follows the same route, but drives at three different speeds: 30, 40 and 50 km per hour, covering an equal distance in each speed segment. The two cars are similar with petrol consumption characteristics (km per litre) shown in the figure below.
Rajiv reaches city B from city A in 4 hours, driving at the speed of 35 km per hour for the first 2 hours and at 45 km per hour for the next two hours. Aditi follows the same route, but drives at three different speeds: 30, 40 and 50 km per hour, covering an equal distance in each speed segment. The two cars are similar with petrol consumption characteristics (km per litre) shown in the figure below.
106. The amount of petrol consumed by Aditi for the journey is
1. 8.3 litres
2. 8.6 litres
3. 8.9 litres
4. 9.2 litres
107. Zoheb would like to drive Aditi's car over the same route from A to B and minimize the petrol consumption for the trip. The amount of petrol required by him is
1. 6.67 litres
2. 7 litres
3. 6.33 litres
4. 6.0 litres
DIRECTIONS for questions 108 to 110: These questions are based on the situation given below:
Recently, Ghosh Babu spent his winter vacation on Kyakya Island. During the vacation, he visited the local casino where he came across a new card game. Two players, using a normal deck of 52 playing cards, play this game. One player is called the Dealer and the other is called the Player. First, the Player picks a card at random from the deck. This is called the base card. The amount in rupees equal to the face value of the base card is called the base amount. The face values of Ace, King, Queen and Jack are ten. For other cards, the face value is the number on the card. Once, the Player picks a card from the deck, the Dealer pays him the base amount. Then the dealer picks a card from the deck and this card is called the top card. If the top card is of the same suit as the base card, the Player pays twice the base amount to the Dealer. If the top card is of the same colour as the base card (but not the same suit) then the Player pays the base amount to the Dealer. If the top card happens to be of a different colour than the base card, the Dealer pays the base amount to the Player.
Ghosh Babu played the game 4 times. First time he picked eight of clubs and the Dealer picked queen of clubs. Second time, he picked ten of hearts and the dealer picked two of spades. Next time, Ghosh Babu picked six of diamonds and the dealer picked ace of hearts. Lastly, he picked eight of spades and the dealer picked jack of spades. Answer the following questions based on these four games.
108. If Ghosh Babu stopped playing the game when his gain would be maximized, the gain in Rs. would have been
1. 12
2. 20
3. 16
4. 4
109. The initial money Ghosh Babu had (before the beginning of the game sessions) was Rs. X. At no point did he have to borrow any money. What is the minimum possible value of X?
1. 16
2. 8
3. 100
4. 24
110. If the final amount of money that Ghosh Babu had with him was Rs. 100, what was the initial amount he had with him?
1. 120
2. 8
3. 4
4. 96
End of Section II
|



